The term Feature Extraction refers to techniques to extract meaningful and informative attributes from images. The
features can be local statistical moments, edges,... or even textures !
Image feature extraction creates representations that are more compact and meaningful than the raw pixel data. The extracted features minimize irrelevant and redundant data, often referred to as "noise", which improves the robustness and accuracy of models (for image classification, object detection,...).
By reducing the data's dimensionality, feature extraction also cuts down the computational resources needed for real-time applications.
This page presents various libraries and tools used for feature extraction, categorized by their main functions. These range from traditional computer vision techniques to machine learning algorithms. Note that the list of tools presented here is non-exhaustive.
Practical example
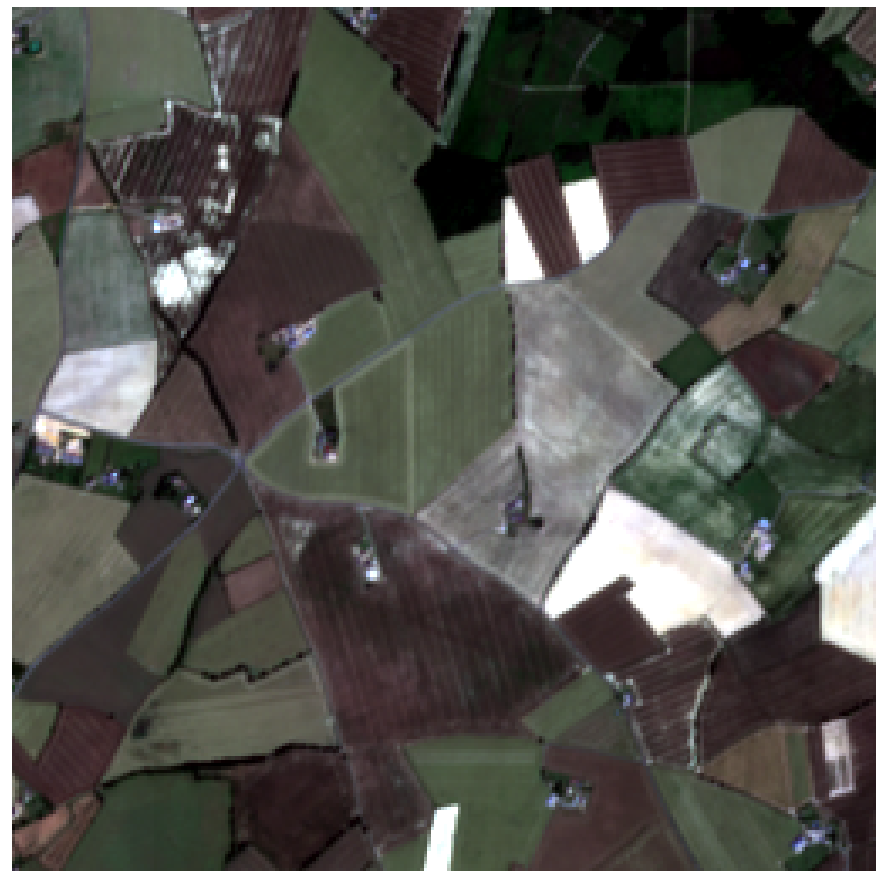
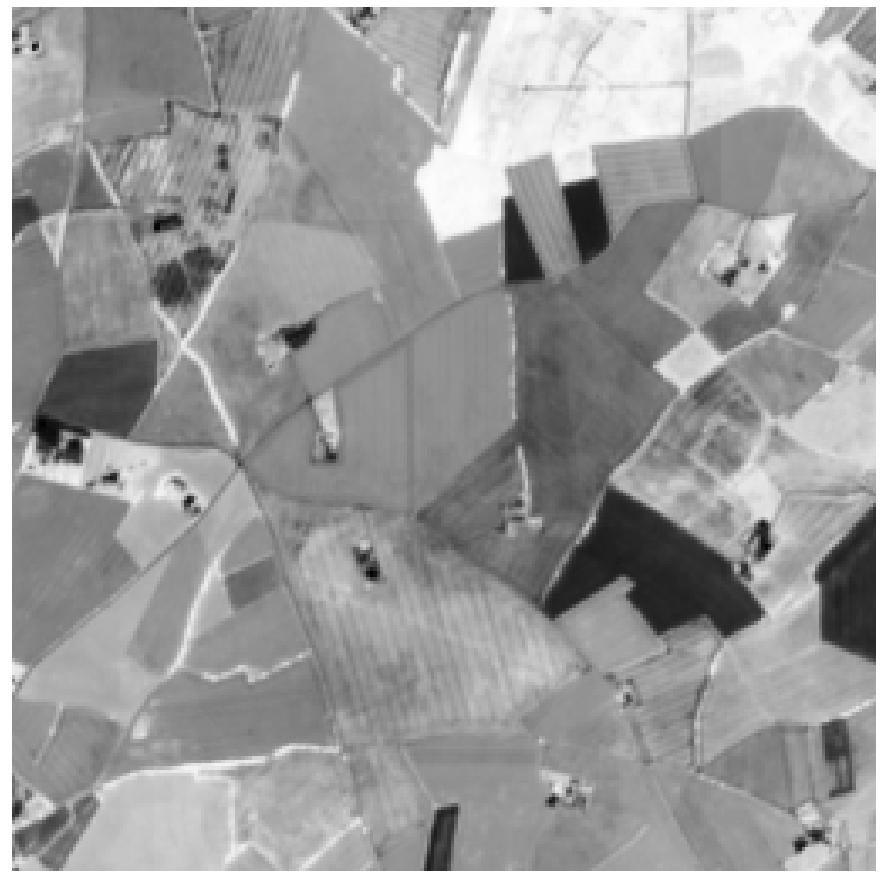
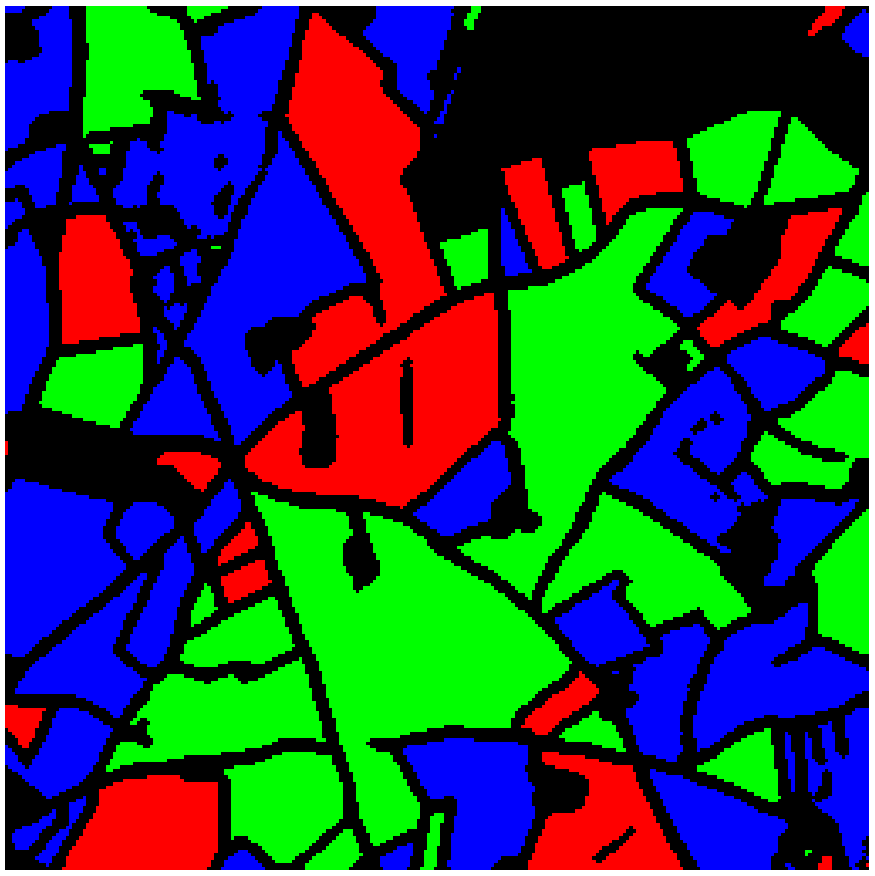
Features extraction can be used for crop segmentation to divide agricultural fields into distinct regions based on crop types or health, enabling precise monitoring and management.
| Original Image | Image manipulation | Segmentation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Bring your own satellite image (Pleiades, WorldView, PNEO, CO3D,...) |
Computation of the NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) from red and near-infrared bands. This metric is used to distinguish land cover types, and to monitor plant health and growth over time. |
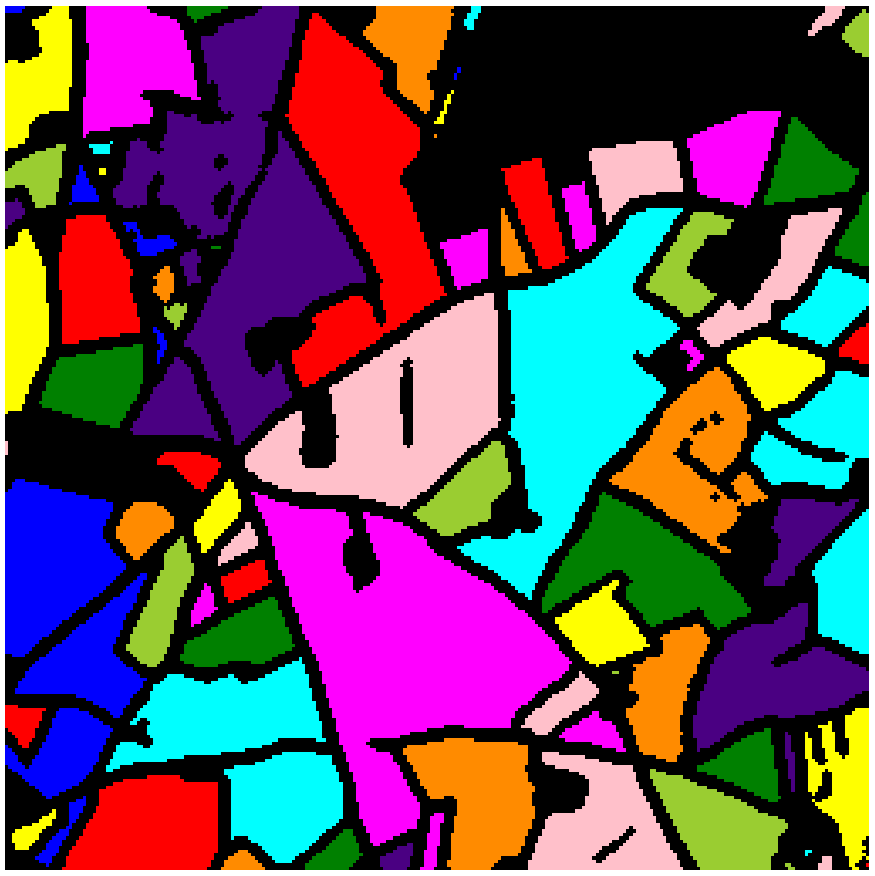
All plots are separated into spatial zones with consistent radiometries using a segmentation method (for exemple Watershed) |
A crop type has been associated to each plot using machine learning (in the image above we used a random forest classifier) |
Image preprocessing
Opening the image
Opening satellite or raster images typically involves reading geospatial data formats and extracting metadata. Please refer to the tools presented in the Data access page.
Image Manipulation (Pixel based)
These tools focus on pixel-wise transformations, band-level operations, and general image processing tasks, such as index calculation and inter-band arithmetic operations.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel based image manipulation |
OTB (Orfeo Toolbox) – otbcli_RadiometricIndices | Radiometric indices extraction |
| Georastertools – radioindice | Compute various vegetation and environmental indices on satellite or raster data | |
| GEOWombat | Efficient computation of indices across large raster datasets | |
| Xarray | Xarray can be really efficient for simple pixel or band level manipulation in coordination with rioxarray or EOReader for example |
Statistics computation (Pixel neighborhood or region based)
These libraries help compute statistical measures from images or geospatial data over pixel neighborhoods or regions:
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Statistics computation | OTB (Orfeo Toolbox) – otbcli_LocalStatisticExtraction | Computes local statistics over a specified pixel neighborhood |
| Georastertools – zonalstats | Compute statistical measures over zones defined by a vector shapefile | |
| DEMcompare | Compare digital elevation models (DEM) through statistical metrics |
Segmentation
Segmentation aims to partition an image into meaningful regions that correspond to objects or areas of interest. Pixels with similar characteristics (such as intensity, texture, or spectral signature) are grouped into coherent segments or regions. In a SAR image, segmentation can be used to delineate flooded versus non-flooded areas by clustering pixels based on their backscatter intensity.
Segmentation methods can range from simple thresholding techniques to more advanced algorithms, such as the watershed method or region-growing approaches.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| 2D/3D rasters | OTB (Orfeo Toolbox) | Segmentation algorithms for remote sensing applications |
| Scikit-Image | Segmentation methods (watershed, k-means, random walker, Chan-Vese...) | |
| OpenCV | Multiple segmentation methods, tutorials are available for thresholding and watershed methods | |
| 2D/3D point cloud | Cloud Compare | Generic point cloud processing software |
| Scikit-learn | Offers a dedicated clustering module | |
Segmentation tools often use morphological operations to enhance results. These operations—such as dilation, erosion, opening, and closing—are especially useful for refining binary masks, removing noise, and separating connected objects (for example. buildings, roads,...).
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Morphological operations | OTB (Orfeo Toolbox) - otbcli_BinaryMorphologicalOperation | Application dedicated to Morphological features extraction |
| Scikit-Image | Contains a dedicated morphology module (closing, opening, skeletonization,...) | |
| OpenCV | Widely used library for preprocessing steps such as filling gaps in segmented regions or eliminating small artifacts in satellite images. A short guide is available available |
Classification (Supervised / Unsupervised Learning)
Classification involves assigning predefined labels to a point, pixel or region based on its features (e.g. spectral values, texture, shape). It is a decision-making process that uses statistical or machine learning models to categorize image data.
In satellite imagery, classification helps determine what each pixel or region represents (e.g., water, forest, urban). A Random Forest classifier can be used to label segments in an image as "urban", "vegetation" or "water".
Machine learning libraries for classifying features extracted from images:
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | OTB (Orfeo Toolbox) | Provides applications to train a supervised or unsupervised classifier from different set of features
and to use the generated classifier for vector data classification. A guide is available |
| Scikit-learn | Traditional machine learning models for supervised and unsupervised classification | |
| iota2 | Automated land cover classification from satellite images | |
| GEOWombat | Scalable tools for satellite image classification using machine learning models across large geospatial datasets | |
| XGBoost, LightGBM | Gradient boosting for efficient and large-scale data classification |