Many people use directly Analysis Ready Data (ARD), often referred as L2 levels in optical images contexts (L2A for Sentinel-2). They are defined by international standards and may vary from one mission to another. But sometimes you have to preprocess data (raw satellite image or products, level 0/1) to work properly on it.
This page presents the main preprocessing steps (from L1 to L2 levels) along with useful tools. Note that the presented tools are non-exhaustive.
Sentinel-2 product levels
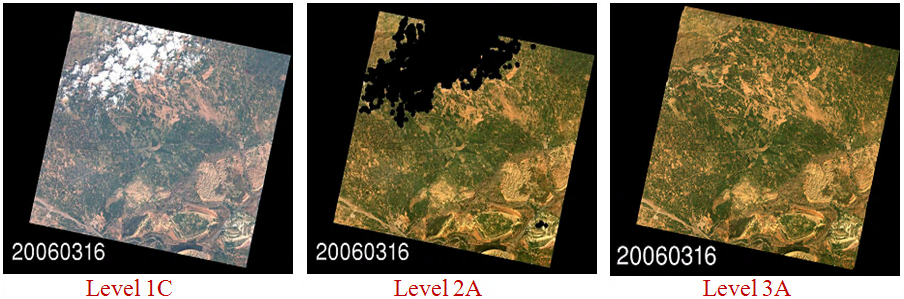
What are the different product levels (L0/L1/L2...)?
CESBIO Multitemp blog presents quite clearly the Product Level names.
In addition the CESBIO website presents a comprehensive serie of posts related to the high resolution optical image production steps here.
Several steps are required to get ready for analysis data. The objective is for example to correct atmospheric aberrations or project images on ground with precise localization.
| Category | Processing | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Radiometry | Radiometric correction | Luminance to reflectance top of atmosphere (TOA) transform. |
| Atmospheric correction | Correction of atmospheric effects to obtain Bottom of atmosphere (BOA or TOC - Top of canopy) from TOA. | |
| Geometry | Sensor model | Refinement of the sensor model (position, in a given referential, and angles of the camera). |
| Projections | Apply geometric information to raw data or change existing projection. | |
| Resampling | Various methods to superimpose images on grids. | |
| Absolute and relative location | Process registration to increase location precision of images. | |
| Homologous points extraction | Estimate displacement between images. | |
| Resolution | Fusion | Methods to sharpen images. |
This table focuses on optical preprocessing, see the end of this page for a word on SAR preprocessing. The following sections detail all given steps, but first let's explore some essential toolboxes that provide the foundation for tackling preprocessing tasks.
Toolboxes
First of all there are some important toolboxes to know as they provides a wide range of tools to manage high resolution optical, multispectral and radar images.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Toolboxes | GDAL | GDAL (Geospatial Data Abstraction Library) is a library for reading, writing and manage raster and vector geospatial data formats. |
| OTB | Orfeo ToolBox (OTB) is an open-source project for state-of-the-art remote sensing. | |
| SNAP | The Sentinel Application Platform (SNAP) is a common architecture for all Sentinel Toolboxes which covers both Radar and Optical imagery. The software is developed by Brockmann Consult, Skywatch, Sensar and C-S. (download page) |
Regarding optical image preprocessing, OTB recipes gives an overview of main preprocessing steps.
Radiometry
Radiometric corrections
Optical radiometric preprocessing (L0 to L1) mainly aims at correcting the digital counts from the sensor response (gain, offset, non-linearity...), it can also include missing or corrupted data (faulty detector, lost packets) interpolation. Most of these corrections are specific to the sensor and require coefficients computed during calibration phase. In consequence, there is few ready-to-use tools, but most of these corrections can be done by using standard image libraries and custom image filters (see PythonStack).
- otbOpticalCalibration: The application allows converting pixel values from DN (for Digital Numbers) to Top Of Atmosphere (TOA) reflectance, and its values lie in the range [0, 1]. It takes into account the sensor gain, sensor spectral response and the solar illuminations.
Optical calibration and Atmospheric correction
Atmospheric correction (L1 to L2) consists in converting satellite images in reflectance TOA (top of atmosphere) to reflectance BOA (bottom of atmosphere aka top of canopy). First step needs to know satellite orbit and altitude, sun elevation (to compute solar time) while second steps involves atmospheric models.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Optical calibration and Atmospheric correction |
otbOpticalCalibration | Performs optical calibration TOA/TOC (Top Of Atmosphere/Top Of Canopy). Supported sensors: QuickBird, Ikonos, WorldView2, Formosat, Spot5, Pleiades, Spot6, Spot7. For other sensors the application also allows providing calibration parameters manually. |
| MAJA | Level-2A processor used for atmospheric correction and cloud-detection which supports various optical products.
|
|
| Sen2cor | Level-2A processor used by ESA for atmospheric correction and cloud-detection of the Sentinel-2 products. | |
| SMAC (legacy) | The Simplified Model for Atmospheric Correction (SMAC) is the perfect model to perform easy and quick atmospheric corrections. It is based on very simple analytic formulas, based on the 5S model. A dedicated page is available on the CESBIO website, along with a set of coefficients. |
Geometry
The following sections gather the tools to geolocate the data and to put various data into the same geometry.
Sensor model
Geometric modeling consits in accounting the sensor acquisition mode caracteristics to convert the raw data (L0) into spatially coherent data array. The refinement step aims at improving the inital localisation obtained from the geometric modeling, by using a digital elevation model, which can be completed by a reference dataset.
These operations can be done with the following librairies:
- LibGeo: LibGEO is designed for rigorous geometric modeling of Earth observation sensors. Interacts with the image geometric model, and is used to build sampling grids. Tools to refine the geometrical models thanks to input homologous points. It contains also tools to manage sampling grids.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric modeling | LibGeo | LibGEO is designed for rigorous geometric modeling of Earth observation sensors. Interacts with the image geometric model, and is used to build sampling grids. Tools to refine the geometrical models thanks to input homologous points. It contains also tools to manage sampling grids. |
| ASGARD | Asgard is “A Sensor Geometry Application Reusable by-Design”. It also embedded the legacy library EOCFI. |
Projections
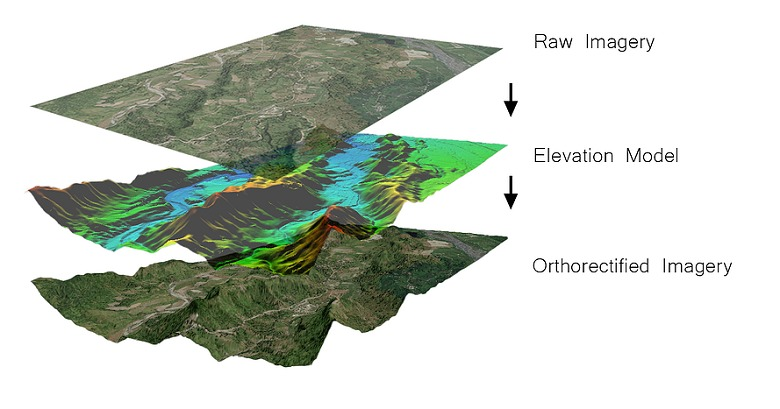
Projection operations apply or modify the data geometry (the projection affects the grid coordinates and the sampling). Ortho-rectification is a specific re-projection, from a sensor geometry image into a ground geometry regular grid (and using a terrain model). The ground geometry regular grid is defined with respect to a map projection.
- otbOrthorectification: Is an OTB application allowing to orthorectifiy image using elipsoide or DEM data.
Resampling
Once the rasters are correctly localized, their grid can still be different, the following tools allow to re-map all the information onto a unique grid so that pixels are superimposable and ready for analysis.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Resampling | gdalwarp | This GDAL tool enables reprojecting and resampling the data, it also allows to crop or mask the data. |
| Rioxarray | Rioxarray provides a various set of tools to resample and project data array. | |
| otbSuperimpose | Combines methods in order to modify the polynomial geometrical model. This model is then used to reproject / resample the image in the chosen geometry. Output images should be perfectly superimposed. |
Absolute and relative location
Image registration consists in correcting the misalignment between the pixels of two inputs images. The displacements estimation can be based on homologous points (as explain above), or by correlation:
- Pandora2d: Pandora2d is a coregistration tool that provide disparity maps for images pairs with a subpixel precision.
Homologous points extraction
Extraction of homologous points enables to find and select salient points into a set of images in order to match them and estimate displacement between the images.
- otbHomologousPointsExtraction: Compute homologous points between images using keypoints
Resolution
Pan-sharpening
Pansharpening is a process of merging high-resolution panchromatic and lower resolution multispectral imagery to create a single high-resolution color image:
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Pan-sharpening | otbPansharpening | This OTB application performs P+XS pansharpening. Algorithms available are: RCS, bayesian fusion and Local Mean and Variance Matching(LMVM). |
| otbBundleToPerfectSensor | Similar as the previous Pansharpening application but specialized for Pleiades products. |
Fusion
Data fusion consists into merging data from various sources or earth observation missions to obtain comparable information. This is very useful to create homogeneous time series.
- Sen2like: Sen2Like allows to generate Sentinel-2 like harmonised/fused surface reflectances with higher periodicity by integrating additional compatible optical mission sensors (in particular Landsat 8/9).
SAR Preprocessing
For an introduction to SAR image preprocessing, you can browse Awesome SAR.
| Function | Tools | Related use cases |
|---|---|---|
| SAR Preprocessing | OTB SAR cookbook | Dedicated to SAR processing and cover both processing and visualization capabilities offered by OTB. |
| Sarpy | SarPy is a basic Python library to read, write, and do simple processing of complex SAR data using the NGA SICD format (standards linked below). | |
| s1Tilling | In many cases, it is also interesting to use both SAR and optical data.S1Tiling allows to tranform Sentinel-1 data into ortho-rectified data resampled on the Sentinel-2 grid to promote joint use of both missions. |
For SAR data in NITF standard format, the use of specific tools is advised